concrete pump cleaning parts, cleaning balls and bullets clean the pipe inner wall concrete and Keeps your work area clean of concrete & wash-out water, we have soft cleaning ball, middle soft cleaning ball, and hard cleaning ball, usually sizes are DN50-DN150, Made from ABS plastic and natural rubber, so they are durable, Can ship via truck freight with your hoses stacked on top, volume capacity can accommodate a full hopper of concrete, standard color is orange , other colors also avaliable. There many kinds of brands, putzmeister, schwing, sany, zoomline, and so on balls, quality and price are promised. Concrete Pump Clean Out Accessories Concrete Pump Clean Out Accessories,Concrete Pump Clean Parts,Concrete Pump Clean Accessories,Small Concrete Pump Accessories Hebei Shengdebaolong International Trading Co.,ltd , https://www.sdblpumpparts.com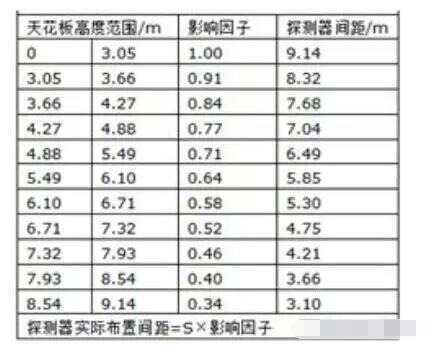
The AP1000 nuclear power plant is the third-generation nuclear power plant designed by Westinghouse. Through the introduction of technology in China, the first batch of 4 units have been started construction, and follow-up plans to build in batches. The design of follow-up projects will be mainly undertaken by the Chinese entity. AP1000 nuclear power plant fire automatic alarm system design mainly uses the American standard. Considering that Chinese projects still need to comply with the relevant mandatory provisions of Chinese standards, and the differences in the requirements for the layout of fire detectors between the two countries' standards, this article compares and analyzes several common fire detector deployment requirements in the Chinese and American standards. The layout of detectors suitable for China's nuclear power projects.
1 Nuclear Power Plant Fire Automatic Alarm System Function
The automatic fire alarm system is an important part of the fire protection system of nuclear power plants. It involves the fire safety of the entire building and is an important safety and security system. The automatic fire alarm system can accurately detect the fire in the early stage of the fire and promptly alarm. It is important for timely organization and rapid evacuation, active and effective control of fire spread, rapid fire extinguishing, and reduction of fire damage and fire risk reduction. effect.
In the rooms or areas where there are fire hazards in each building of a nuclear power plant, fire detectors are reasonably selected according to the characteristics of the fire in the fire detection area, and a fixed installation of fire detectors is used for continuous monitoring. In case of fire, fire alarm signals are automatically sent out immediately, enabling operators and firefighters to quickly and accurately detect early fires, determine the specific location of the fire, and provide corresponding fire alarms on the fire alarm control panel and the local analog display panel. And device status indication. Simultaneously start the fire linkage device and automatically or manually control the fire extinguishing device to extinguish the fire. The fire automatic alarm system can also conduct fire emergency broadcasts as required, guide the evacuation of personnel and the fire extinguishing actions of firefighters.
2 Status of Automatic Fire Alarm System for AP1000 Nuclear Power Plant
The automatic fire alarm system design of the AP1000 nuclear power plant mainly adopts the US National Standard NFPA72-2002 "National Fire Alarm Code", while the project in China also needs to comply with the Chinese Standard GB50116-2013 "Fire Automatic Alarm System Design Specification." There are differences between the requirements of the two standards in the layout of fire detectors. For several kinds of fire detectors commonly used in nuclear power plants, such as temperature detectors, infrared beam smoke detectors, and temperature sensors, according to the layout of fire detectors under different plant structures, comparative analysis of Chinese standards and American Standards Requirement for the Arrangement of Several Kinds of Fire Detectors.
3 Fire detector layout requirements comparative analysis
3.1 Smoke detector
The arrangement of the point type smoke detector needs to consider the influence of the surrounding environment. The surrounding environment's temperature, humidity, airflow speed, etc. will affect the detector's sensitivity and reliability.
3.1.1 American Standard Requirements
1) The horizontal distance from the side wall when installing on the ceiling should not be less than 100mm; when the detector is arranged on the side wall, the height from the ceiling should be between 100mm and 300mm. When the point-type smoke detectors are arranged on smooth ceilings, they are generally arranged according to the standard spacing S=9.1m. The distance from the detector to the wall edge does not exceed 0.5S. The distance from any point in the protection area to the detector is not more than 0.7S. . According to the actual conditions during layout, such as ceiling height, beam structure, joist structure, and high airflow speed, the spacing between detectors should be appropriately changed.
2) The ceiling height influences the arrangement spacing of the detectors, but no detailed value is given in NFPA 72. Here, reference can be made to the effect of the ceiling height on the spot-type temperature detectors, see Table 1. At the same time, the spacing of the detectors is not less than 0.4 times the height of the fire to the ceiling.
3) Beams and joists have the same effect on the arrangement of point-type smoke detectors.
Table 1 Effect of ceiling height on point-type temperature detector
For horizontal ceilings, if the ceiling height does not exceed 3.66m and the beam height does not exceed 300mm, the spacing of the detector in the direction parallel to the beam is still S, in the direction perpendicular to the beam, and the spacing is S/2; If the ceiling height exceeds 3.66m, or the beam height exceeds 300mm, point-type smoke detectors should be placed in each beam area. For sloping ceilings and beams parallel to the inclined plane, the spacing of the detectors is determined according to the pitch of the horizontal ceiling; the height of the ceiling is calculated as the average height; when the inclination exceeds 10°, the distance from the detector to the wall is not limited by 0.5S; Take the horizontal projection value. For sloping ceilings and beams that are perpendicular to the sloping face, the detector placement pitch is determined based on the pitch of the horizontal ceiling; the ceiling height is calculated as the average height.
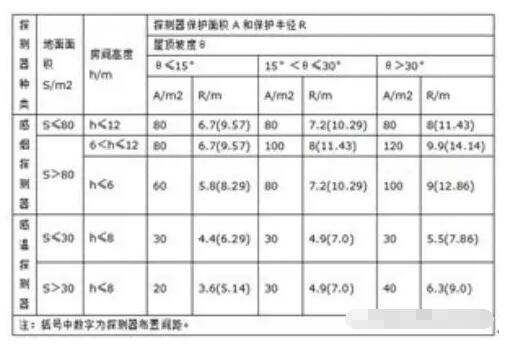
Table 2 Detector Protection Area and Protection Radius
3.1.2 Chinese Standard Requirements
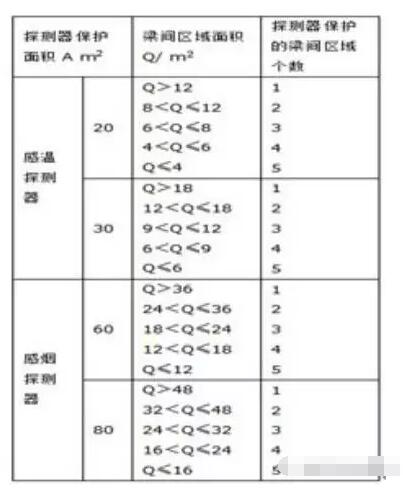
1) The horizontal distance from the detector to the wall and the edge of the beam should not be less than 0.5m; there should be no obstructions within 0.5m around the detector; the horizontal distance from the detector to the air-conditioning air outlet should not be less than 1.5m, and should be close to the back The tuyere is installed; the horizontal distance from the detector to the aperture of the multi-hole ventilation ceiling shall not be less than 0.5m; 2) The influence of the ceiling height on the spacing of the detectors is given in Table 2. 3) When the detector is arranged on the beamed ceiling, When the height of the beam protruding ceiling is less than 200mm, the influence of the beam on the protection area of ​​the detector is not taken into account; when the height of the beam protruding from the ceiling is 200-600mm, the influence of the beam on the protection area of ​​the detector and the protection of a detector are determined according to Table 3. The number of areas between beams; when the height of the beams protruding from the ceiling exceeds 600 mm, the detectors are arranged in separate areas for each section of the beams that are partitioned; when the distance between the beams is less than 1 m, the influence of beams on the protection area of ​​the detectors is not taken into account. .
3.1.3 Contrast results
Through comparison of the standards, it can be seen that according to the US standard, the scope around the detector outside 0.1m can have structures such as walls and beams. According to Chinese standards, the scope outside the detector can have structures such as walls and beams or shelters outside the radius of 0.5m. When the object is actually arranged, in order to save investment, the vertical distance from the detector to the wall, the beam edge, etc. generally takes 0.5S. This distance is generally greater than 0.5m, so the above factors have little effect on the spacing of the detectors.
The main influence of the spacing of the detector arrangement comes from the height of the ceiling. Taking the ceiling of 5m height as an example, the spacing of detectors required in the US standard is 6.49m, and the spacing of detectors required in the Chinese standard is 9.57m. According to American standards, when the beam height exceeds 300 mm, each beam area should be used as a separate area for the detector arrangement. According to the Chinese standard, when the beam height exceeds 600 mm, each beam area is used as a separate area for the detector arrangement. Therefore, in this respect, American standards are more stringent than Chinese standards.
Table 3 Effect of Beam on Detector Protection Area
3.2 Infrared beam smoke detector
When the beam-type smoke detector is arranged on a horizontal or sloping ceiling, it can be considered equivalently as a row of point-type smoke detectors.
3.2.1 American Standard Requirements
The beam length of the beam smoke detector does not exceed the limit established by the manufacturer. When arranged, the beam spacing is generally taken as S = 18.3m, and the beam distance from the wall is no more than S/2. The transmitting and receiving ends of the beam smoke detector are generally fixed on both ends of the wall and can also be suspended from the ceiling. When suspended from the ceiling, the distance between the transmitting end and the receiving end is not more than S/4. .
3.2.2 Chinese Standard Requirements
The vertical distance from the beam axis of the infrared beam smoke detector to the ceiling should be 0.3-1.0m, and the height from the ground should not exceed 20m. The horizontal distance between two adjacent infrared beam smoke detectors should not exceed 14m. The horizontal distance from the detector to the side wall should not exceed 7m and should not be less than 0.5m. The distance between the transmitter and receiver of the detector should not exceed 100m.
3.2.3 Comparison result
In the arrangement of infrared beam smoke detectors, when arranged in accordance with Chinese standards, the spacing between the detectors is smaller, the density of the arranged detectors is greater, and the detection reliability is also higher. Therefore, we believe that the Chinese standards in this area should be stricter than the American standards. In addition, slight vibration of infrared beam smoke detectors during operation may affect the performance of the detectors. Therefore, the detectors should be arranged on a firm foundation and should be fixed on the solid wall surface. The suspension installation method is not recommended.
3.3 temperature detector
3.3.1 U.S. Standard Requirements
1) The horizontal distance of the point type temperature detector from the side wall when installed on the ceiling should not be less than 100mm; when the detector is arranged on the side wall, the height from the ceiling should be between 100~300mm. The spacing distance S of the spot-type thermal detectors should comply with the manufacturer's recommended distance, which is generally determined by a standard fire test. When the point-type temperature detector is arranged on the smooth ceiling, the distance from the detector to the wall shall not exceed 0.5S, and the distance from any point in the protection area to the detector shall not be greater than 0.7S. According to the influence of ceiling height, beam structure, etc., the spacing S of the detectors should be adjusted properly. 2) The effect of ceiling height on the spacing of point-type thermal detectors is given in Table 1. 3) For the joist structure, point-type thermal detectors are arranged in a direction parallel to the beam without affecting the distance, still S; In the direction perpendicular to the beam, the detector spacing should be halved to S/2. For beam structures, if the beam height does not exceed 100mm, consider the smooth ceiling; if the beam height exceeds 100mm, the spacing of the detectors in the direction perpendicular to the beam should not exceed 2S/3; if the beam height exceeds 460mm and the beam If the center spacing is greater than 2.4m, each beam area is arranged as a separate area.
3.3.2 China Standard Requirements
Please refer to section 3.1.2 for the layout requirements of point type temperature detectors.
3.3.3 Comparison results
By comparing the US and China standards, it can be seen that according to the US standard, the area around the detector outside 0.1m can have structures such as walls and beams. According to Chinese standards, the area outside the detector at 0.5m can have structures such as walls and beams. In case of actual arrangement, in order to save investment, the vertical distance from the detector to the wall, beam edge, etc. generally takes 0.5S. This distance is generally greater than 0.5m, so the above factors have little effect on the spacing of the detectors. .
The main influence of the spacing of the detector arrangement comes from the height of the ceiling. Taking the ceiling of 5m height as an example, the spacing of detectors required in the US standard is 6.49m, and the spacing of detectors required in the Chinese standard is 6.29m. According to American standards, when the beam height exceeds 460 mm, each beam area should be used as a separate area for the detector arrangement. According to the Chinese standard, when the beam height exceeds 600 mm, each beam area is used as a separate area for the detector arrangement. Therefore, in this respect, American standards are more stringent than Chinese standards.
4 Conclusion
Through the above comparison of the Chinese and American standards, it can be seen that the US standard is more stringent than the Chinese standard for the use of point-type smoke detectors and point-type temperature-sensitive detectors that are relatively common and used in the most amount. For infrared beam smoke detectors, the arrangement pitch specified in the Chinese standard is more stringent than the arrangement pitch specified in the U.S. standard.
Due to the U.S. standard and the Chinese standard, the ceiling height has a great influence on the spacing of the detectors. Taking the nuclear island auxiliary plant as an example, the ceiling height of the auxiliary plant on the nuclear island is 4.5m to 5.1m. According to the calculation of the smooth roof, according to the US standard, the arrangement distance of the smoke detectors is 7.04m to 6.49m; according to the Chinese standard, the arrangement spacing of the smoke detectors is 8.29m, and the American standards are more stringent than the Chinese standards. For temperature sensitive detectors, the spacing between layouts in the U.S. standard is determined by fire tests or manufacturer's recommendations and cannot be compared with the specific values ​​in Chinese standards.
To sum up, for most situations, American standards are stricter than Chinese standards. If these aspects are designed with reference to American standards, they can meet the requirements of Chinese standards. Since the total investment in the automatic fire alarm system of nuclear power plants accounts for a small proportion of the total investment in the project, both the Chinese and American standards can be referenced in the design and reference can be made to more stringent requirements to ensure the timeliness of detection of fires and systems. The reliability. At the same time, other detectors not mentioned in this article, such as flame detectors, gas detectors, smoke detectors installed in ventilation ducts, etc., shall be arranged in accordance with the manufacturer's proposed scheme so that the detector can reach Best performance, more efficient detection of fire, and protection of personal and property safety in nuclear power plants.
references
[1] Lai Qi. Comparison of the layout design of tank farms in the Sino-American regulations[J]. Southern Energy Development, 2016(1).
[2] Wan Quan. The working principle and selection analysis of common fire detectors[J]. Archives, 2013(1):101-102.
[3] Shang Shengmei, Wang Haiqing, Liu Junfang. Research on the optimal arrangement of FPSO fire gas detectors[J]. Oil and Gas Chemicals, 2013, 42(3): 311-315.
[4] Yao Mingqi. Analysis of false alarm of fire detectors in Sanmen nuclear power project [J]. Modern Manufacturing, 2015(3):30-32.