Real Time Nucleic Acid Diagnosis System Qpcr System,Polymerase Chain Reaction,Real Time Pcr Thermocyclers,Real Time Nucleic Acid Diagnosis System Changzhou Taqlab Biotechnology Co.,ltd , https://www.dinaipcr.com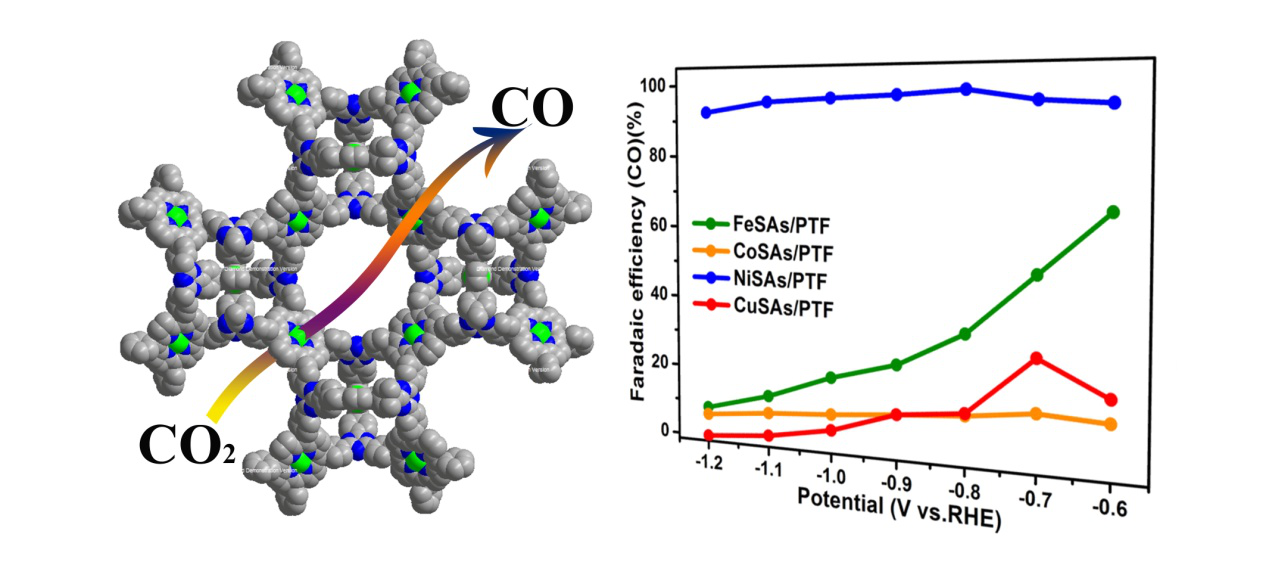
[ Instrument Network Instrument Development ] In recent years, due to the large-scale use of traditional energy sources, the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere has increased sharply, leading to problems such as greenhouse effect and environmental climate deterioration. Therefore, measures need to be taken to reduce the concentration of CO2. Converting CO2 into usable chemicals is a way to turn waste into treasure. The use of electricity generated by sustainable energy for electrocatalytic CO2 conversion has the advantages of mildness and environmental protection. However, there are still shortcomings such as low selectivity, high overpotential, and low current density, so finding a suitable catalyst is the key.
Monoatomic catalysts have the highest atomic utilization and exhibit high activity and high selectivity in many catalytic reactions. However, the activity of different monoatomic metal catalysts is different, and the reasons remain to be clarified. Recently, the research team of Fujian Institute of Material Structure and State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Cao Rong and Huang Yuanbiao, under the support of the Ministry of Science and Technology Key Research and Development Program, the Fund Committee, the Chinese Academy of Sciences Pioneer and Frontier Program, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences Youth Promotion Project The team prepared a stable monoatomic method for a porous porphyrinyl triazine framework material (ACS Energy Lett., 2018, 3, 883 889; J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 1252) to prepare the vector. Stable series of single-atom catalysts such as Ni, Cu, Fe and Co, and systematically studied the performance of electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. Compared with other metal monoatomic catalysts, the prepared Ni monoatomic catalysts have a CO-Faraday efficiency of more than 90% over a wide voltage test range (-0.6 - -1.2 V vs. RHE), and are in - The selectivity is close to 100% (98%) at 0.8 V and the TOF value is as high as 13462 h-1 at -1.2 V. The calculations show that the electrochemical potentials of Ni and Fe catalysts are smaller than those of Co and Cu catalysts, so Ni and Fe catalysts show higher activity; while Ni catalysts have higher energy barrier ratios for HER than CO2RR, so hydrogen is well suppressed. The energy barrier of the desorption of CO by the Fe catalyst is high, so the Ni catalyst exhibits a high CO2RR ability.
This work provides a new idea for the design of synthetic and efficient single-atom non-precious metal catalysts, and provides an important reference for the development of new high-efficiency electrocatalysts. The relevant research results were published in the China Chemical Society's flagship magazine CCS Chem., 2019, 1, 384–395.